Robotic Process Automation (RPA) started as a powerful way to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks. Artificial Intelligence (AI) brought learning, prediction, and human-like perception into software. When you combine RPA in AI, the result is far more transformative than either technology alone: intelligent automation. Today, organizations are also leveraging virtual agents AI and Contact Center AI - Customer Service Innovations to streamline customer interactions and enhance operational efficiency.
Beyond customer service, AI-powered cloud platforms are reshaping the way businesses store, process, and analyze massive amounts of data, making operations faster and more scalable. Innovations in advanced computing technologies allow AI systems to run more efficiently, supporting smarter decision-making across departments. Companies are embracing predictive marketing technologies and AI-assisted advertising solutions to create targeted campaigns, anticipate consumer needs, and strengthen engagement across online and offline channels. Similarly, AI-driven financial solutions are helping organizations automate accounting tasks, manage investments, and enhance risk management with real-time insights and smarter decision-making.
This article explains what RPA in AI really means, how the two fit together, and the concrete benefits organizations can expect when they adopt intelligent automation strategically, not just in contact centers but across cloud computing, emerging technologies, marketing, and finance.
Top 10 AI Contact Center Solutions Leveraging RPA in AI to Transform Customer Service Operations
When it comes to RPA in AI and enhancing contact center efficiency, several platforms stand out for their ability to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. Here’s a list of top solutions currently shaping the future of intelligent customer service:
1. Bright Pattern – AI-Powered Contact Center Platform
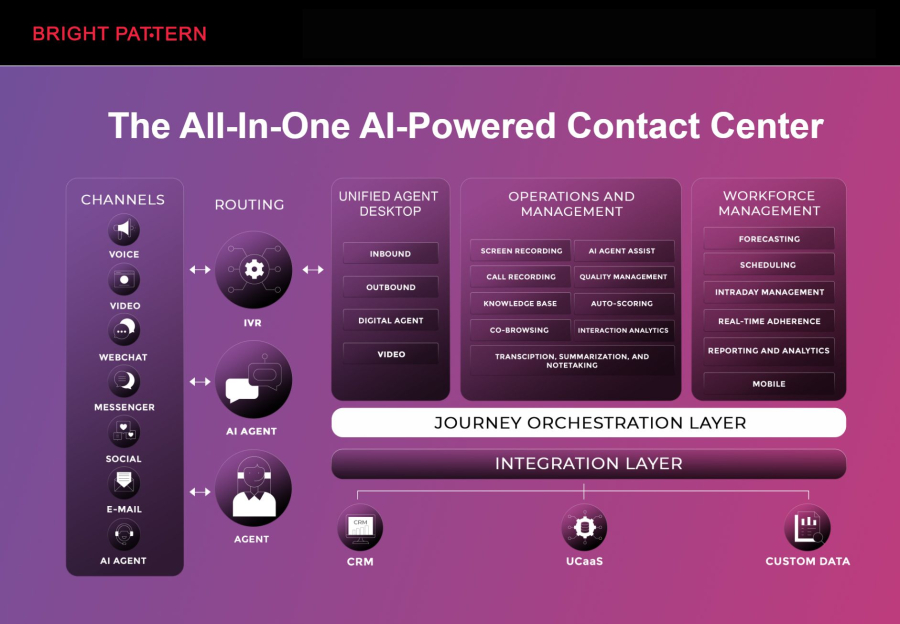
Bright Pattern is a leading platform that combines RPA in AI with virtual agents AI to deliver seamless, omnichannel customer experiences. Their solution helps businesses reduce repetitive tasks, improve agent efficiency, and provide faster, more personalized service.
Key Highlights:
- Omnichannel support: Voice, chat, email, SMS, and social messaging in one unified platform.
- AI-driven virtual agents: Automates routine inquiries and escalates complex issues to human agents.
- Real-time analytics: Insights into customer interactions and operational efficiency.
- RPA integration: Automates repetitive backend processes, such as data entry, ticket updates, and workflow triggers.
- Scalable cloud architecture: Supports growing businesses without infrastructure constraints.
Bright Pattern is especially effective for organizations looking to merge intelligent automation with AI contact center solutions, ensuring consistent and personalized experiences across all customer touchpoints.
2. Genesys Cloud CX
A comprehensive cloud contact center solution integrating AI chatbots, predictive routing, and RPA capabilities to enhance customer service and agent productivity.
3. Five9 Intelligent Cloud Contact Center
Provides AI-assisted virtual agents, workforce optimization, and RPA integrations to automate repetitive tasks and improve service efficiency.
4. NICE CXone
Offers AI-driven automation, virtual agents, and advanced analytics to optimize contact center operations and customer satisfaction.
5. Cisco Contact Center AI
Combines AI chatbots, analytics, and RPA tools to streamline workflows, reduce handle times, and enhance the agent experience.
6. Avaya OneCloud
Supports AI-powered automation and virtual assistants while integrating RPA to manage routine tasks across customer service channels.
7. Talkdesk AI Cloud
Leverages AI and RPA to improve contact center workflows, offer predictive insights, and deliver a seamless omnichannel experience.
8. RingCentral Contact Center
Integrates intelligent automation and AI tools to assist agents, automate repetitive processes, and provide real-time analytics.
9. 8x8 Contact Center AI
Offers virtual agent AI, workflow automation with RPA, and analytics dashboards to enhance customer engagement and operational efficiency.
10. SAP Contact Center Solutions
Provides AI-powered customer service automation, including RPA for backend processes, analytics, and virtual agent support.
What Is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)is software that mimics the actions a human performs on a computer. Instead of a person clicking, typing, and copying data across applications, a software robot follows the same steps.
Typical characteristics of RPA include:
- Rule-basedworkflows that follow clear if-then logic.
- Structured datainputs, such as spreadsheets, databases, or forms with consistent fields.
- User interface interactionwith existing systems, without needing to rewrite legacy applications.
- High volume, repetitive taskslike data entry, reconciliation, and report generation.
On its own, RPA excels at tasks that are stable, predictable, and clearly defined. But it struggles when data is unstructured, decisions are ambiguous, or rules change frequently. That is where AI enters.
What Is AI in the Context of RPA?
Artificial Intelligence (AI)refers to systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. In the context of RPA, we are usually talking about specific AI capabilities rather than general intelligence.
Key AI technologies that enhance RPA include:
- Machine learningto find patterns in data, make predictions, or classify items without hard-coded rules.
- Natural language processing (NLP)to understand and generate human language in emails, chat messages, and documents.
- Computer visionto interpret images or scanned documents, extract fields, and validate visual information.
- Optical character recognition (OCR)to convert printed or handwritten text into digital, machine-readable data.
- Conversational AIsuch as chatbots or virtual assistants that interact with users in real time.
When these capabilities are embedded into RPA workflows, robots are no longer limited to simple tasks; they can understand, decide, and adapt within defined boundaries.
From RPA to Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation(sometimes called intelligent process automation or IPA) is the combination of RPA with AI technologies to automate more complex, end-to-end business processes.
Instead of automating only the last step of a process (for example, entering data into a system), intelligent automation can handle:
- Reading and understanding documents.
- Interpreting emails and messages.
- Making decisions based on models and business rules.
- Routing work intelligently to the right system or person.
The result is a powerful synergy:AI provides the “brain,” and RPA provides the “hands.”
Key Business Benefits of Combining RPA and AI
When organizations integrate RPA and AI, they do more than save time on individual tasks. They reshape how work flows across the entire business. Below are some of the most compelling benefits.
1. End-to-End Process Automation
Traditional RPA often targets isolated steps in a process. With AI, you can automate far more of the journey from start to finish. For example:
- A customer sends an email request with attachments.
- NLP and OCR interpret the message and documents.
- AI models classify the request and determine priority.
- RPA bots log into multiple systems, update records, and trigger responses.
- The customer receives a personalized confirmation or resolution.
This kind of orchestration reduces manual handoffs, shortens cycle times, and gives customers faster, more consistent outcomes.
2. Higher Accuracy and Reduced Risk
Both RPA and AI contribute tohigher accuracywhen configured and monitored properly.
- RPAexecutes steps exactly as designed, eliminating many copy-paste errors or skipped fields.
- AImodels can be trained and tested against large data sets to reduce misclassification and flag anomalies for human review.
This is especially powerful in compliance-heavy areas such as finance, healthcare, and insurance, where consistent documentation and audit trails are critical. Automated logs from bots also make it easier to trace what happened and when.
3. Scalability and Operational Resilience
RPA bots can run 24 / 7, and you can scale them up or down in response to demand peaks. When AI is integrated, those bots can handle a wider range of scenarios without constant rule changes.
Business benefits include:
- Handling seasonal spikesin workload without rushing to hire and train temporary staff.
- Maintaining service levelswhen teams are remote, distributed, or operating under disruption.
- Improving business continuitybecause critical processes are documented, automated, and less vulnerable to key-person risk.
4. Enhanced Customer and Employee Experience
Intelligent automation makes interactions smoother for both customers and employees.
- For customers, AI-driven chatbots and automated workflows deliver instant responses, accurate information, and faster resolutions.
- For employees, repetitive tasks such as searching, copying, and reconciling are offloaded to bots, freeing people for higher value, more creative work.
The combination often leads to higher satisfaction on both sides: customers get speed and consistency, while teams feel more engaged and less bogged down by routine tasks.
5. Better Use of Data for Decision-Making
RPA creates structured, reliable data trails. AI turns that data into insight. Together they help organizations move from gut-feel decisions to data-driven strategies.
Examples include:
- Identifying process bottlenecks and opportunities for further automation.
- Spotting patterns in customer behavior and adjusting offerings.
- Predicting workload and allocating capacity more efficiently.
The more processes you automate and instrument with data, the richer your analytics and AI models become.
Real-World Style Use Cases for RPA in AI
Organizations across industries are applying intelligent automation in practical, tangible ways. Here are some illustrative use cases.
Customer Service and Support
- Email triage: NLP reads inbound emails, classifies intent (for example, complaint, request, general question), extracts key details, and sends them to RPA bots for routing and response.
- Chatbots with back-end automation: A conversational AI assistant answers common questions and triggers RPA bots to reset passwords, update records, or initiate refunds.
- Case summarization: AI summarizes long support interactions, and RPA updates case management tools, reducing after-call work for agents.
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing: OCR and AI extract fields from invoices (such as vendor name, amount, and dates). RPA validates data against purchase orders and posts entries into the accounting system.
- Expense auditing: Machine learning models flag unusual or non-compliant expenses, and RPA bots perform initial checks, leaving only exceptions for human review.
- Financial close support: RPA gathers balances and statements; AI highlights anomalies or trends that accountants should investigate.
Human Resources
- Recruitment screening: AI analyzes resumes to identify skills and experience; RPA schedules interviews and updates applicant tracking systems.
- Employee onboarding: RPA creates user accounts, provisions access, and enrolls benefits; AI chatbots answer common policy questions from new hires.
- HR request handling: NLP interprets internal emails or messages, and RPA completes routine updates such as address changes or leave balances.
Operations and Supply Chain
- Order management: AI predicts demand based on history and external signals; RPA bots place replenishment orders and update inventory across systems.
- Logistics tracking: RPA collects shipment information from carriers; AI models predict delays, and alerts are sent proactively to customers or planners.
- Quality checks: Computer vision inspects images from production lines; exceptions trigger RPA workflows for documentation and corrective actions.
Compliance and Risk Management
- Document review: AI scans contracts or forms for key clauses or missing items; RPA routes documents to the right stakeholders for sign-off.
- Transaction monitoring: Machine learning highlights suspicious patterns; RPA gathers supporting information to help compliance teams investigate.
- Regulatory reporting: RPA consolidates data from multiple systems; AI checks for inconsistencies before reports are submitted.
How RPA and AI Work Together Under the Hood
To design effective intelligent automation, it helps to understand how RPA and AI components fit together technically. While architectures vary, many solutions share the following building blocks.
|
Layer |
Role in Intelligent Automation |
|
Input and capture |
Collects emails, documents, forms, images, and system events that will trigger automation. |
|
AI / cognitive services |
Uses OCR, NLP, machine learning, and computer vision to interpret content, classify items, and recommend actions. |
|
Decision and orchestration |
Combines AI outputs with business rules to decide what should happen next and which bot or person should handle it. |
|
RPA execution |
Software robots log into applications, move data, update records, and complete tasks across systems. |
|
Monitoring and analytics |
Tracks performance, error rates, throughput, and business outcomes for continuous improvement. |
In practice, AI services may be built into the RPA platform or integrated as external components. The key is that they exchange information through clear interfaces so that decisions and actions remain transparent and controllable.
Getting Started with RPA and AI: A Practical Roadmap
Adopting intelligent automation is most successful when approached as a structured, business-led initiative rather than a purely technical experiment. Here is a step-by-step roadmap.
1. Clarify Business Objectives
Start by answering questions like:
- Which outcomes matter most right now: cost savings, speed, quality, customer experience, or risk reduction?
- Which processes are critical to those outcomes?
- Where are employees spending time on repetitive, manual work?
Clear goals will guide your choice of processes, tools, and success metrics.
2. Identify and Prioritize Use Cases
Look for processes that are:
- Stable enough to automate, but currently manual and time-consuming.
- High volume or high impact on customers and revenue.
- Dependent on structured or semi-structured data that AI can interpret.
Start with a small portfolio of use cases that can demonstrate value within a manageable timeframe. This builds momentum and support for broader adoption.
3. Map and Simplify the Process
Before automating, map the existing workflow clearly. Often you will find steps that can be removed or simplified. Automating a flawed process tends to lock in inefficiency.
Ask stakeholders:
- Which steps truly add value?
- Where do errors and rework occur most often?
- Which decisions require human judgment, and which could be supported by models and rules?
4. Decide Where AI Adds the Most Value
Not every task needs AI. In each process, identify:
- Inputs that are unstructured (such as emails and scanned documents) where OCR and NLP are helpful.
- Decisions that rely on patterns in historical data where machine learning could assist.
- Interactions where a conversational interface could reduce friction for users.
Use RPA for straightforward, deterministic tasks and introduce AI selectively where it meaningfully extends what can be automated.
5. Build, Test, and Iterate
When implementing intelligent automation:
- Develop a proof of concept for one or two use cases.
- Test with real data and a representative group of users or subject matter experts.
- Measure time saved, error reduction, and user feedback.
- Refine process logic, AI models, and bot behavior before scaling.
An iterative approach reduces risk and ensures that solutions are grounded in actual business needs.
6. Scale with Governance
As you expand RPA and AI across the organization, establish governance to keep initiatives aligned and secure. Consider:
- Standards for documenting automations and models.
- Security and access controls for bots and data.
- Monitoring mechanisms to ensure ongoing accuracy and compliance.
- A central team or center of excellence to share best practices.
Best Practices for Successful Intelligent Automation
Organizations that see the most benefit from RPA in AI tend to follow a few common practices.
Combine Human Expertise with Automation
Rather than aiming to replace people, design automations thataugment human capabilities. Keep humans involved in:
- Defining business rules and exceptions.
- Reviewing high-risk or ambiguous decisions flagged by AI.
- Improving models and workflows based on real-world outcomes.
Design for Transparency and Control
Make it easy to understand how decisions are made and to intervene when necessary. That can include:
- Clear dashboards showing which bots are running and what tasks they perform.
- Documented logic for RPA workflows and AI-driven decisions.
- Approval steps for sensitive actions such as payments and data changes.
Invest in Data Quality
AI models rely on data. The cleaner and more complete your data, the more accurate and trustworthy your automations will be. Focus on:
- Standardizing data fields and formats across systems.
- Reducing duplicate or inconsistent records.
- Setting up feedback loops so data errors are corrected at the source.
Prepare People and Culture
Intelligent automation changes how work gets done. To maximize benefits:
- Communicate clearly about goals, benefits, and timelines.
- Involve employees in designing and testing automations.
- Provide training so people can work effectively with bots and AI tools.
- Highlight success stories where automation removed frustration and created new opportunities.
Measuring the ROI of RPA in AI
To build a strong business case and guide further investment, measure both quantitative and qualitative impact.
Quantitative Metrics
- Time savedper transaction or process.
- Throughput(how many items are processed per day or week).
- Error ratesbefore and after automation.
- Cost per transactionand overall operating costs.
- Process cycle timefrom initiation to completion.
Qualitative and Strategic Benefits
- Employee satisfactionas routine work is reduced.
- Customer satisfactionand loyalty driven by faster, more consistent service.
- Improved compliancethrough standardized, auditable processes.
- New capabilitiessuch as real-time analytics or self-service options that were difficult before.
Capturing both types of value helps stakeholders see intelligent automation not only as a cost reduction tool but as a strategic enabler.
Emerging Trends in RPA and AI
The landscape of RPA and AI continues to evolve quickly. Several trends are making intelligent automation more accessible and powerful.
Low-Code and Citizen Development
Many modern platforms offerlow-code interfacesfor building bots and integrating AI models. This allows business users, not just developers, to contribute directly to automation initiatives, with appropriate governance in place.
Process and Task Mining
Process miningandtask miningtools analyze system logs and user activity to identify automation opportunities and reveal how processes actually run. Combined with RPA and AI, they enable data-driven decisions about what and how to automate.
More Context-Aware Automation
As AI models become better at understanding context, intelligent automation can handle more nuanced tasks. That includes recognizing customer sentiment, prioritizing work based on business impact, and adapting responses to different scenarios while still operating within defined controls.
Closer Integration with Enterprise Platforms
RPA and AI capabilities are increasingly built directly into core business applications, such as ERP and CRM systems. This reduces integration effort and makes it easier to deploy automation where business users already work.
Conclusion: Turning RPA and AI into a Strategic Advantage
RPA and AI, when combined thoughtfully, do far more than automate simple tasks. They enableintelligent automationthat can transform how your organization operates, serves customers, and empowers employees.
By starting with clear goals, focusing on high-impact use cases, and blending human expertise with digital workers, you can unlock:
- Faster, more reliable processes from end to end.
- Richer insights from the data your operations generate every day.
- A better experience for both customers and the teams who support them.
For organizations ready to reimagine work,RPA in AIis not just a technology upgrade. It is a practical, scalable path to building a more agile, resilient, and competitive business.
